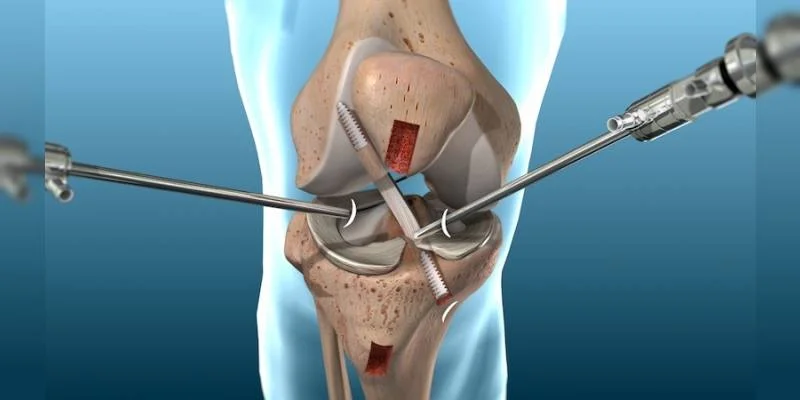
What is Arthroscopy?
Arthroscopy, also known as arthroscopic surgery, is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used by doctors to diagnose and treat joint problems. During this procedure, a tiny camera (arthroscope) is inserted into the joint through a small incision. This allows the surgeon to view the inside of the joint on a monitor, diagnose the problem, and perform the necessary treatment.
Arthroscopy is frequently used for joints such as the knee, shoulder, elbow, ankle, and wrist. It's recommended for patients who have joint injuries, inflammation, or chronic damage that cannot be res olved with non-surgical treatments like physical therapy or medication.
When is Arthroscopy Needed?
Arthroscopy may be recommended if:
- You have joint pain, swelling, or stiffness that hasn't improved with other treatments
- You've injured a joint (e.g., torn cartilage, ACL damage)
- You have persistent inflammation in the joint
- You have conditions such as arthritis or tendonitis
- Your mobility is affected due to joint damage
Common Conditions Treated with Arthroscopy
- Knee Injuries : Torn meniscus, ACL reconstruction, cartilage damage
- Shoulder Problems : Rotator cuff tears, frozen shoulder, tendonitis, impingement
- Elbow Issues : Tennis elbow, ligament tears, joint arthritis
- Hip Problems : Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), labral tears
- Ankle Injuries : Ligament tears, arthritis, chronic ankle instability
- Wrist Conditions : Carpal tunnel, ligament damage, arthritis
Types of Arthroscopy
1. Knee Arthroscopy
Two small incisions are made to insert the arthroscope and surgical instruments. It's commonly used to treat torn cartilage, meniscus injuries, ACL reconstruction, and cartilage damage.
2. Shoulder Arthroscopy
Ideal for rotator cuff tears, shoulder instability, and impingement syndromes. It reduces recovery t ime due to smaller incisions and minimal muscle disruption.
3. Hip Arthroscopy
Primarily used for femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) and labral tears. It's a newer technique gaini ng popularity for hip problems.
4. Ankle Arthroscopy
Used to treat conditions like chronic ankle instability, arthritis, and ligament damage.
5. Wrist Arthroscopy
Often performed to treat conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome, ligament tears, and arthritis.
Dr. Chandresh Sharma's Approach to Arthroscopy
Dr. Chandresh Sharma is a renowned arthroscopy surgeon with years of experience in successfully trea ting joint injuries and diseases. His approach includes:
- Personalized Care : Tailoring treatments to each patient's needs, whether for professional athletes or everyday individuals.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques : Focus on minimal disruption to healthy tissue for faster healing an d reduced complications.
Dr. Sharma uses cutting-edge technology and internationally certified instruments to ensure the best possible results for his patients.
Step-by-Step Arthroscopy Procedure
1. Pre-Surgical Evaluation
- Detailed medical history and physical exam
- Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to assess joint damage
- Anesthesia consultation
2. Surgical Procedure
- Performed under spinal or general anesthesia
- Small incisions (usually 2-3) are made near the joint
- The arthroscope (small camera) and surgical instruments are inserted into the joint
- Damaged tissue is repaired, or abnormalities are addressed with minimal disruption
- The procedure typically lasts between 30 minutes to 2 hours, depending on the complexity
3. Post-Surgical Care and Rehabilitation
- Most patients can go home the same day or after a short stay (24 hours)
- Pain management is prescribed, and physical therapy is recommended for recovery
- Full recovery time varies depending on the joint treated and the extent of the injury
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery time varies based on the joint and type of surgery. Typically:
- Initial Recovery : Patients are encouraged to move the joint gently soon after surgery to prevent stiffness.
- Physical Therapy : Critical for strengthening muscles and improving mobility.
- Return to Activity : Light activities are often resumed within a few weeks, but high-impact activit ies may take 3-6 months.
Risks and Complications
Although arthroscopy is generally safe, there are some risks, including:
- Infection
- Bleeding or blood clots
- Nerve injury
- Stiffness or reduced range of motion
- Joint instability (rare)
Dr. Sharma follows strict protocols to minimize these risks and ensure a smooth recovery process.
Long-Term Outcomes and Life After Arthroscopy
Arthroscopic surgery generally provides long-term relief from joint pain and improved mobility. With proper rehabilitation, patients can return to their usual activities, including sports, work, and d aily routines. The success rate for arthroscopy is very high, particularly with the expertise of a s killed surgeon like Dr. Sharma.
Why Choose Dr. Chandresh Sharma?
- Fellowship-Trained :Specialized training in advanced arthroscopic techniques.
- Proven Expertise :Highly rated for successful surgeries and excellent patient outcomes.
- State-of-the-Art Facilities :Use of the latest technology and techniques.
- Patient-Centered Care :Focus on educating patients and ensuring optimal recovery.
Dr. Sharma is widely regarded as one of the best arthroscopy surgeons in Ahmedabad and Jodhpur, know n for his skill, care, and positive outcomes.
Testimonials: What Patients Say
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Pain is usually minimal and well-controlled with medication. Most patients report significant pai n relief after the procedure.
Recovery time depends on the joint treated and the complexity of the procedure, but most patients resume normal activities within 4-6 weeks.
Most patients can return to light sports or activities within 3-6 months, depending on the joint and type of injury.
The incisions are small, typically resulting in minimal scarring and faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery.







